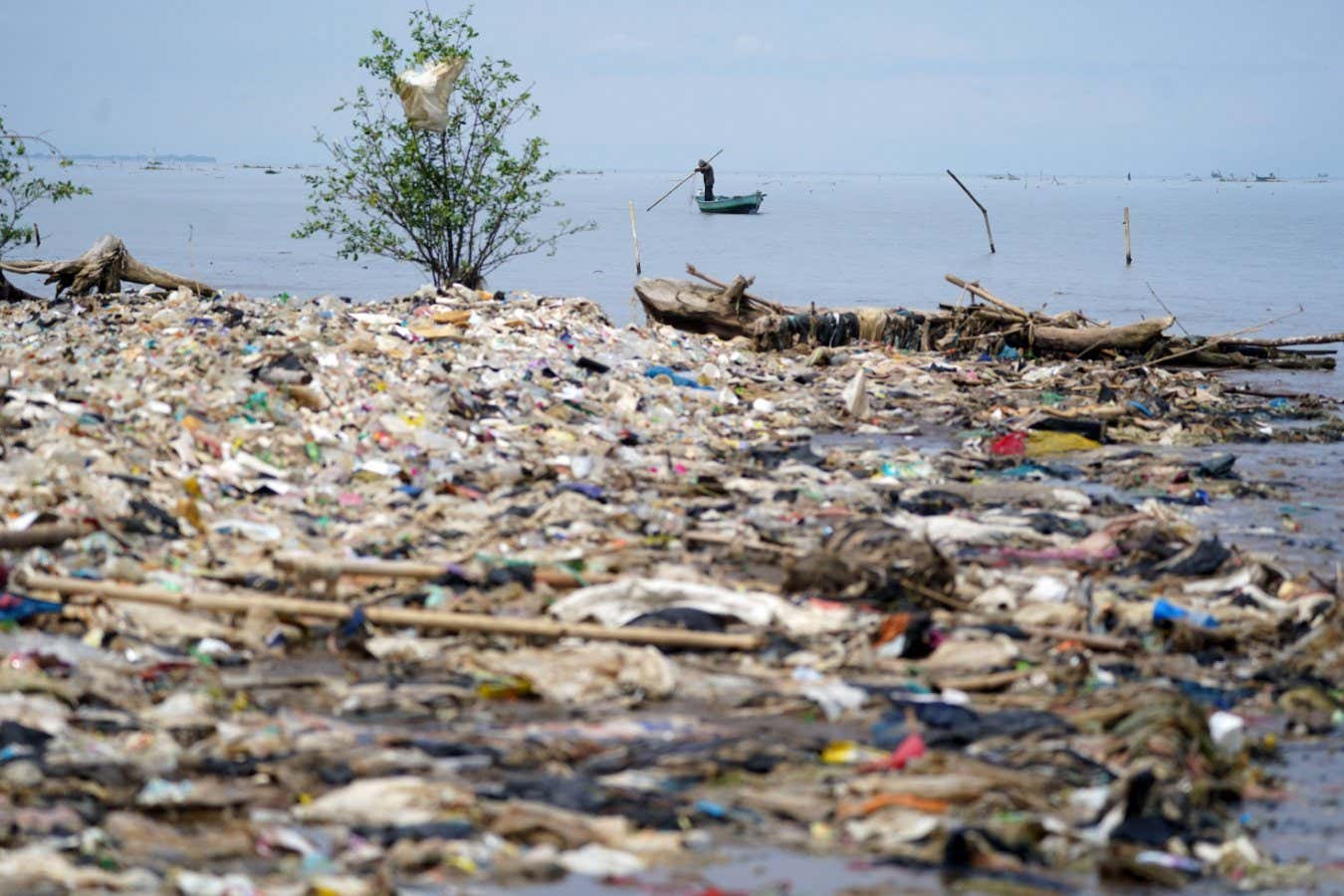
Plastic waste in Indonesia
PA Images / Alamy
The world currently produces more than 50 million tonnes of “mismanaged” plastic waste each year, and some researchers project this flood of plastic pollution will double by mid-century – but they also say that, if countries can agree to adopt four key policies during global plastic treaty negotiations this week, we could slash that number by 90 per cent.
Plastic pollution ends up clogging ecosystems on land and at sea. “This has an impact on every level of the food chain, from phytoplankton cells to humans,” says Sarah-Jeanne Royer at the University of California, San Diego. Plastics are also responsible for about 5 per cent of greenhouse gas emissions.
That’s why most of the world’s countries are meeting in Busan, South Korea this week to hammer out the final details of a global treaty aimed at ending plastic pollution. In 2022, 175 countries already agreed to adopt the legally binding treaty and have spent the past two years debating exactly what it should require, with particular disagreements over setting limits on the production of new plastic.
To bring more clarity to the debate, Douglas McCauley at the University of California, Santa Barbara and his colleagues used an artificial intelligence model trained on economic data to test how the policies under consideration would affect global plastic pollution. “I wasn’t convinced that [eliminating plastic pollution] was actually possible,” says McCauley. “But it turns out you can get pretty darn close.”
According to their projections, under current conditions, plastic pollution is set to roughly double to between 100 and 139 million tonnes by 2050. But a combination of four policies, all of which are still on the table in the current treaty draft, were enough to reduce this by more than 90 per cent.
The most impactful of these was a mandate that plastic products contain at least 40 per cent recycled material. That rule alone cut plastic pollution in half by mid-century. This effect is so significant because it cuts demand for newly made or “virgin” plastic while also spurring demand for recycled materials, says McCauley. “Suddenly there’s a giant global market for recycling.”
But recycling on its own wasn’t sufficient. “If your target is to end plastic pollution, you need to do things across the entire lifecycle,” he says. Deeper cuts required limiting production of virgin plastics to 2020 levels. This production cap cut plastic pollution by around 60 million tonnes per year by the middle of the century, according to the model. This change also had the greatest impact on greenhouse gas emissions from plastic production, as extracting fossil fuels and turning them into virgin plastics involves emissions-intensive processes.
A third policy, spending $50 billion on waste management, reduced pollution by nearly the same amount as the production cap – especially if these funds were spent in low-income countries with poor infrastructure, which are also the most inundated by plastic pollution. “When you start talking about global finance, [the amount of money needed] is not that big,” says McCauley. “Building a sanitary landfill is not like building a port.”
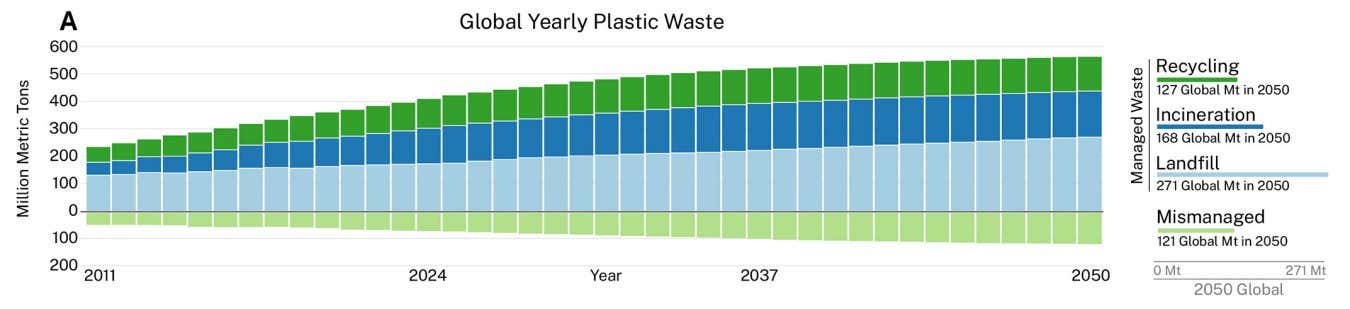
Plastic waste is increasing, and though some is recycled or destroyed, a large portion is “mismanaged” and piles up as plastic pollution
A. Samuel Pottinger et al.
Finally, a small tax on plastic packaging cut pollution by tens of millions of tonnes. The researchers based this estimate on case studies of how people reduced their plastic use in response to similar taxes, such as a 5 cent fee on single-use plastic bags in Washington DC. Money raised by such a tax could also be used to pay for other changes, like building out waste management infrastructure or improving recycling systems.
Royer, who was not involved with the study, says she thinks those policies would all help. Reducing the use of single-use plastic such as grocery bags or plastic forks via a tax or a ban could also make a difference, she says. “If we look at plastic pollution in general, 40 per cent of the plastic being produced is single-use items.”
However, she points out local rules alone will never solve the problem. For instance, California banned some single-use plastic bags a decade ago and this year banned all such bags. But most of the plastic pollution that washes up on its beaches originates outside the state: California’s plastic waste generally drifts across the Pacific from Asia or is flotsam left by the fishing industry. “There’s no border,” says Royer.
That’s where a global treaty comes in. The researchers showed how implementing different policies across the world would cut down on three things: the volume of mismanaged plastic waste, the production of new plastics, and plastic-related greenhouse gas emissions. The four key policies in combination, seen in the graph below, reduced all three measures, and in particular slashed mismanaged waste by 91 per cent.





