 BBC
BBCI’m on the hunt for a microbial saviour – a type of virus that can treat infections rather than cause them.
We all know the viral bad guys – Covid, flu, norovirus, herpes, chicken pox, measles… the list goes on.
But there’s a type of virus that’s not interested in infiltrating our bodies, instead it preys on bacteria.
They’re known as bacteria eaters, or bacteriophage, or commonly as phage.
Capturing them could give us new ways of treating infections, including superbugs that are becoming incurable.
So, how to catch a killer?
I’ve been promised it’s surprisingly easy. The team at the Phage Collection Project sent me some vials to collect samples, along with a pair of gloves. All I need to do is hunt for some dirty water, the dirtier the better, dip the vials in and screw on the lid.

I tried a couple of ponds, the juice from a worm-composting bin and then I needed my dirtiest sample. I didn’t flush the toilet after a poo and left it for a couple of hours. I pop on a glove and hold my breath as I go in for the final sample. Strict hygiene instructions, including vigorous hand-washing, were followed, at all times.
The vials were packaged up for collection and then three days later I headed off to the University of Southampton to see what was inside.
“They were a bit dirty when I received them,” phage scientist Michelle Lin tells me as we don our blue lab-coats and matching gloves to go into the Containment Level 2 microbiology laboratory.
We grab my samples from the fridge, which look much clearer now they have been filtered of any… debris. “It’s fine, it’s needed,” Michelle, who had the unpleasant job, reassures me.

Filtering is the first step in looking for phage, next they get served dinner – a cocktail of yummy bacteria – to help them grow in number.
Now comes the really cool bit – finding a useful phage. The scientists have been working with the local hospital to collect bacteria from patients with troublesome infections.
Michelle grabs a petri dish that’s growing bacteria from a patient with a painful, urinary tract infection that keeps coming back.
And to my amazement – one of the phage I collected from my toilet was able to kill this infection in the lab.
“The way to see that the phage has infected bacteria is you get these zones where the bacteria are not growing and that’s because they’ve been killed by the phage,” says Michelle.
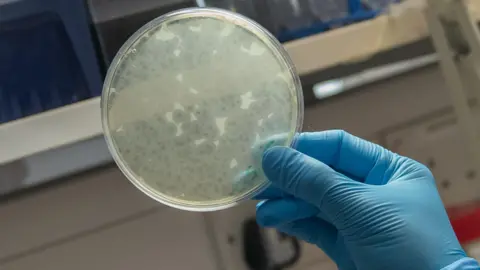
You can see the leopard print pattern in the petri dish where the phage have been making light work of a bacterial infection that modern medicine was struggling to shift.
“As crazy as it sounds, well done to the toilet sample,” says Michelle with great delight.
And when I was offered the chance to name the phage, well of course it’s the Gallagher-phage.
“Sounds amazing to me,” says Michelle.
So far this is all good fun in the laboratory, but could my phage ever be given to a patient?
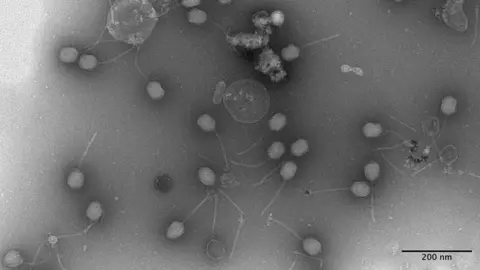
“Yes and I hope so,” says associate professor Dr Franklin Nobrega as we look at images of my phage captured with an electron microscope.

“Your phage, already in just 24 hours, we were able to get in a high concentration and able to be a very good killer, which means this is very promising for patients, so thank you,” said Dr Nobrega.
Phage remind me of a moon lander – a big capsule on spindly legs – just instead of landing on the surface of the moon they use their legs to select their victim.
They then hijack the bacteria and transform it into a mass-production factory for more phage, which burst out of their host, killing it in the process.
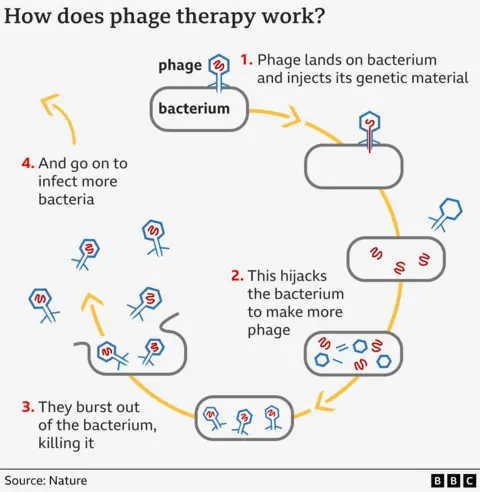
There are pros and cons to phage. They reproduce as they go along so you don’t need constant doses like you would with drugs.
They are also very picky eaters. You need a precise match between phage and the strain of bacteria you’re trying to treat whereas antibiotics tend to kill everything good and bad. So it is harder to find the right phage, but if you do it comes with fewer side effects.
Dr Nobrega tells me infected wounds are a “very good application” for phage because you can apply them directly to the injury, but they can also be inhaled via a nebuliser to treat lung infections or to target urinary tract infections “which is our target currently”.
 Getty Images
Getty ImagesPhage – the friendly virus
Phage science may sound new and exciting, but it is actually a century old idea stemming from the discoveries of Felix d’Hérelle and Frederick Twort in the 1910s.
Bacteriophage therapy was a branch of medicine and the idea was compelling. Even as late as the 1940s there was an active pharmaceutical industry in western countries trying to produce phage-therapy to defeat bacterial infections.
However, it was rapidly eclipsed by the wonder-drug of the 20th century.
“Antibiotics were working so well that most people said ‘why bother’,” says Dr Nobrega.
 University of Southampton
University of SouthamptonWork on phage therapy continued in places like Georgia and there are individual accounts of it working wonders; but there hasn’t been the same depth of medical research and clinical trials as there have for drugs.
But just as the initial success of antibiotics suppressed phage research, the failure of antibiotics is reigniting excitement at their potential.
More than a million people a year are already dying from infections caused by microbes that are resistant to treatment – it’s known as the “silent pandemic”. By 2050, that figure is projected to reach 10 million a year.
This “antibiotic apocalypse” would mean common infections could kill again and undermine modern medicine. The drugs are also used to make organ transplants, open surgery and chemotherapy possible.
“The predictions around antibiotic resistance are very frightening, but the reality is we’re seeing it now and it’s only going to get worse,” says Prof Paul Elkington, the director of the institute for medical innovation at the University of Southampton.

He is also a doctor with a speciality in lung medicine and is already at the point where – after a year of treatment and turning to ever more toxic and less effective antibiotics – “in the end you have to have a conversation [and say] ‘we can’t treat this infection, we’re really sorry'”.
He says we can’t rely solely on antibiotics in the future and phage are a potential alternative.
But he warns the steps needed to get from the laboratory and into patients are “uncharted”.
Things are changing. Phage therapy is available in the UK on compassionate grounds when other treatments have failed. And the drugs regulator – The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency – has published its first official rules to support the development of phage therapy.
“If one looks 15-20 years into the future, with the emerging methodologies, it’s going to be possible for them to be much more widely available and for doctors to prescribe phage instead of antibiotics for some infections,” says Prof Elkington.
If you want to see if you can find a friendly virus too then The Phage Collection Project are launching their new sampling kits at the Summer Science Exhibition taking place this week at the Royal Society and through their website.
“Antimicrobial resistance is something that could affect all of us,” says Esme Brinsden from the Phage Collection Project, “when the public get involved they may just find the next phage that can help treat and save a patient’s life”.
Photography by the BBC’s Emma Lynch







